Have you ever wondered how scientific advancements can help when nature takes a different path?
Having a child is a cherished dream for Indians, but sometimes, due to multiple changing lifestyles and other factors, dreams need some help. That’s where IVF (in-vitro fertilisation) comes in!
IVF offers hope for all couples facing difficulty in normal conception. It is an advanced medical procedure in which the sperm and egg are fertilised in a laboratory under the guidance of fertility specialists. Once it grows, the fertilised egg is successfully implanted back into the uterus, resulting in a successful pregnancy.
However, IVF is not just a one-day process. It has multiple stages and steps, including retrieving eggs from ovaries, combining them with sperm in the lab, and placing them back into the uterus.
Are you struggling with normal conception due to male infertility or female infertility issues?
If yes, fertility specialists at Yaami Fertility have the best, customised IVF treatment options for you, assuring successful pregnancy with maximum success rates (varying on the individual’s health).
Furthermore, if you’re looking for the details of the IVF process and stages, the sections in this blog below have everything for your clarity. Scroll down to the details to know more!
In this blog, we will discuss the process of IVF and what are the 5 stages of IVF.
What are The 5 Stages of IVF?
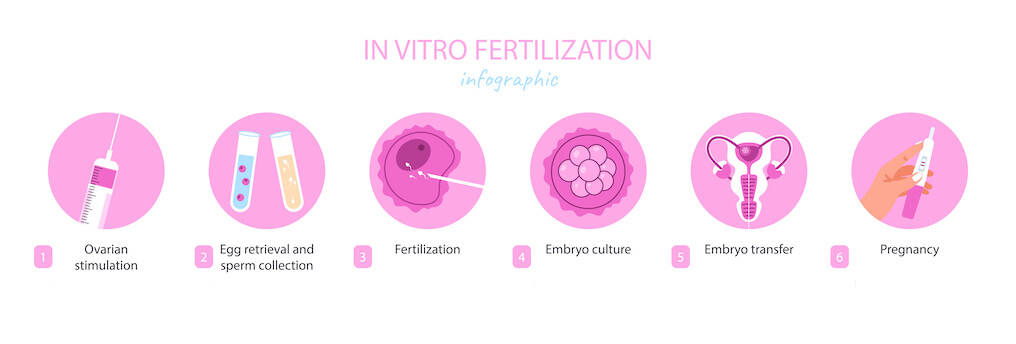
1. Ovarian Stimulation
Ovarian stimulation is the first and the critical IVF stage. Also known as “Controlled Ovarian Stimulation,” the process aims at producing multiple eggs in a single menstrual cycle.
Unlike a typical menstrual cycle where only one egg matures, the goal is to secure more mature eggs. This is achieved using medications, optimising the chances of obtaining several healthy eggs for fertilisation and, consequently, a successful pregnancy.
When is Ovarian Stimulation Done?
The process commences at the beginning of a woman’s menstrual cycle and is monitored for about 8-12 days, depending on the individual’s response.
What Does Ovarian Stimulation Involve?
A series of hormone injections, primarily FSH (Follicle follicle-stimulating hormone), are administered to the woman to encourage her ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Regular ultrasounds and blood tests track these eggs’ growth and maturity.
How is Ovarian Stimulation Performed?
Hormones, particularly FSH (Follicle follicle-stimulating hormone), are administered to the woman to prompt her ovaries. The amount and duration of these hormones are adjusted according to the woman’s unique hormonal levels and ovarian reserve.
Why is Ovarian Stimulation Essential?
The primary goal is to procure several eggs. This allows for a superior selection of healthy eggs ready for fertilisation, giving us more embryos, which amplify the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Other Important Information:
– Side-effects: Some might experience mild side-effects like bloating, mood swings, or tenderness near the ovaries, but these are usually short-lived.
– Monitoring: Regular clinic visits are vital during this phase. Ultrasounds help track the follicles’ size, and blood tests determine hormone levels.
– Adjustments: Depending on the body’s reaction, alterations in medication type, dosage, or duration might be required.
2. Egg Retrieval
The second stage in the journey of IVF is the egg retrieval process. With ovarian stimulation, multiple eggs are produced. These matured eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries to fertilise in the laboratory.
When is Egg Retrieval Done?
The egg retrieval process is scheduled approximately 34 to 36 hours after the final hormone injection and just before the woman naturally releases her egg (ovulation). This timing is critical to maximise the chances of retrieving mature eggs.
Egg Retrieval Process –
Using an ultrasound-guided needle through the vaginal wall, mature egg follicles are aspirated from the ovaries. The procedure lasts around 10-20 minutes and is usually performed under sedation or light anaesthesia for the patient’s comfort.
How is Egg Retrieval Performed?
The woman is generally given a mild sedative or anaesthesia to ensure she’s comfortable and pain-free. The entire procedure lasts about 10-20 minutes. It’s minimally invasive and is carried out as an outpatient procedure, meaning an overnight hospital stay is unnecessary.
Why is Egg Retrieval Essential?
This step is crucial because the eggs retrieved are the ones that will be fertilised in the lab. The more mature eggs are collected, the higher the chances of obtaining healthy embryos, increasing the probability of a successful pregnancy.
Other Important Information:
– Recovery: Post-procedure, some women might feel drowsy due to sedation or experience slight discomfort. It’s generally advised to rest for the day.
– Risks: While generally safe, there’s a minimal risk of infection, bleeding, or injury to surrounding organs. However, with skilled professionals, these risks are substantially minimised.
– Outcome: Typically, several eggs are retrieved, but not all may be suitable for fertilisation. Quality rather than quantity matters at this stage.
Read Also: पीरियड के कितने दिन बाद आईवीएफ(IVF) होता है? – Yaami IVF
3. Sperm Collection/Retrieval
Sperm collection is the next step, following egg retrieval, which involves collecting sperm samples that will be used to fertilise the collected mature eggs from the ovaries. Just as egg retrieval is vital for women, ensuring the quality and quantity of sperm is paramount for a successful IVF cycle.
When is Sperm Collection Done?
The sperm collection usually coincides with the day of the woman’s egg retrieval, ensuring the sperm’s freshness for the impending fertilisation process.
What Does the Process Entail?
For most men, sperm is collected through ejaculation. The man is usually asked to produce a sample in a sterile container provided by the fertility clinic.
How is Sperm Collection Performed?
The standard method is through ejaculation. However, if there are challenges in producing a sample this way, or if there are no sperm in the ejaculate due to medical reasons, minor surgical methods might be employed. One standard method is TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration), where a needle extracts sperm directly from the testes.
Why is Sperm Collection Essential?
Without quality sperm, the fertilisation of the egg is not possible. The collected sperm undergoes a rigorous evaluation process, where only the healthiest and most mobile sperm are chosen for fertilisation, increasing the chances of IVF success.
Other Important Information:
– Preparation: Men are generally advised to abstain from ejaculation for 1-2 days before the collection to ensure the best sperm quality.
– Risks: For standard collection, there are minimal risks. However, there might be mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising for procedures like TESA or PESA.
– Evaluation: Once collected, the sperm sample undergoes a thorough examination to measure count, motility, and morphology.
4. Fertilisation & Embryo Development
In this stage, the collected sperm and eggs unite for fertilisation, a magical moment where potential life begins. This step also signifies the culmination of previous steps and the start of a new life in the lab.
When Does Fertilisation Occur?
Once the eggs are retrieved and the sperm is collected, they are promptly combined in a specialised laboratory dish. The fertilisation usually happens within a few hours.
What is the Fertilization Process?
The collected sperm sample is prepared in a lab, selecting the healthiest and most mobile sperms. These selected sperms are then introduced to the retrieved eggs. Out of this, the sperm penetrates an egg, leading to fertilisation.
How is Fertilization Monitored?
Embryologists carefully watch over the eggs for signs of fertilisation. By the next day, they can identify which eggs have been successfully fertilised by spotting two pronuclei in the egg’s centre.
Why is the Lab Environment Crucial?
The lab environment plays a critical role in this phase. Precise temperature, humidity, and gas composition levels are maintained to mimic the human body’s conditions, ensuring the best possible environment for fertilisation and early embryo development.
Other Vital Information:
– Grading: Embryologists will grade embryos based on their appearance and growth rate, helping select the best for transfer.
– Risks: Not all eggs will fertilise, and not all fertilised eggs will develop into healthy embryos. This natural attrition is why multiple eggs are retrieved.
– Embryo Storage: If there are additional high-quality embryos, they can be cryopreserved (frozen) for future IVF cycles.
5. Embryo Transfer
The climax of the IVF journey, embryo transfer, is the last IVF stage, where the embryo, nurtured and developed with utmost care in the laboratory, is placed into the woman’s womb. This step brings countless families closer to welcoming a new member.
When Does Embryo Transfer Take Place?
Usually, the embryo transfer occurs 3 to 5 days post-fertilisation. However, the specific day is chosen based on the embryo’s development and the conditions of the uterus. The most mature and healthy embryo, often at the blastocyst stage (Day 5 or 6), is chosen for the transfer. In many cases, embryos are frozen and transferred after 2 months if needed.
How is embryo transfer done?
The chosen healthy embryo(s) are delicately placed into the woman’s uterus using a soft, thin catheter. This is usually a painless process and does not require anaesthesia, although some women might experience slight discomfort.
How is the Transfer Done?
The doctor, guided by ultrasound, will ensure the embryo is placed in the optimal location inside the uterus. Precision is key, as it increases the chances of successful implantation, and therefore, a fertility expert’s assistance is advised for the procedure.
Why is Embryo Transfer Significant?
This step is crucial because it determines whether the embryo will implant and result in a pregnancy. The days following the transfer are vital, as the embryo needs to attach itself to the uterine lining, marking the beginning of pregnancy.
Other Essential Information:
– Number of Embryos: Based on the embryo quality, the woman’s age, and previous IVF attempts, one or more embryos might be transferred. However, to reduce the risks associated with multiple pregnancies, the trend is to transfer fewer high-quality embryos.
– Aftercare: Post-transfer, the woman is advised to relax for a short period at the clinic. Light activities are encouraged in the days following the transfer, and any intense physical exertion is generally discouraged.
– The Wait: After the transfer, there’s a waiting period (often called the “two-week wait”) before a pregnancy test can determine the procedure’s success.
Read Also: What is Test Tube Baby (IVF)?
Risk Factors Associated with IVF

While In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a remarkable medical advancement that has brought joy to countless families, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with the procedure.
– Multiple Pregnancies:
Since more than one egg is transferred to the uterus during the IVF procedure, it can increase the chances of multiple pregnancies, with twins, triplets or even more. This, furthermore, raises complications for both the mother and the babies.
– OHSS (Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome):
Fertility drugs given during the IVF procedure might cause swelling and pain in the ovaries, and severe OHSS can further lead to abdominal pain, rapid weight gain, nausea, and shortness of breath. With advances in the types of medications, these days, the incidence of OHSS is extremely low.
– Ectopic Pregnancy:
When the fertilised egg is implanted outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube or somewhere else, it is called an ectopic pregnancy, which can cause life-threatening issues.
– Birth Defects:
Children conceived through IVF may have a slightly higher risk of congenital disabilities than those conceived naturally. The causes for this increased risk mostly relate to the reason for infertility rather than IVF procedures.
– Emotional and Psychological Strain:
The IVF process can be emotionally taxing. The anticipation, treatments, and waiting periods can challenge mental well-being and relationships.
– Miscarriage:
The risk of miscarriage for IVF treatments is similar to natural conception but increases with the mother’s age.
Conclusion: 5 stages of IVF
Choosing IVF is a big decision for many families in India. It’s good to know all the steps and risks involved. If you’re thinking about this journey, Yaami Fertility is here to help. With their expert team and care, they have helped many families grow. It’s essential to be well-informed and to choose the proper support.
Yaami Fertility is committed to making your IVF journey as smooth and successful as possible.
Let’s work together to bring your dream of a family to life. Connect with the fertility experts at Yaami Fertility now to know more about the best and most affordable IVF treatments.

Dr. Swati Singh (MBBS, MD – Obstetrics & Gynecology, DNB, FRM, Diploma in Reproductive Medicine and Embryology – Germany) is a leading Infertility Specialist and Gynecologist with over 18 years of experience. As Co-Founder and Senior Consultant at Yaami Fertility & IVF Center, Indore, she offers advanced fertility care including IUI, IVF, ICSI, and management of female reproductive disorders. Known for her compassionate and patient-first approach, Dr. Swati combines global training with deep clinical expertise. She is also actively involved in women’s health advocacy, medical research, and promoting awareness about reproductive wellness and fertility treatments.











